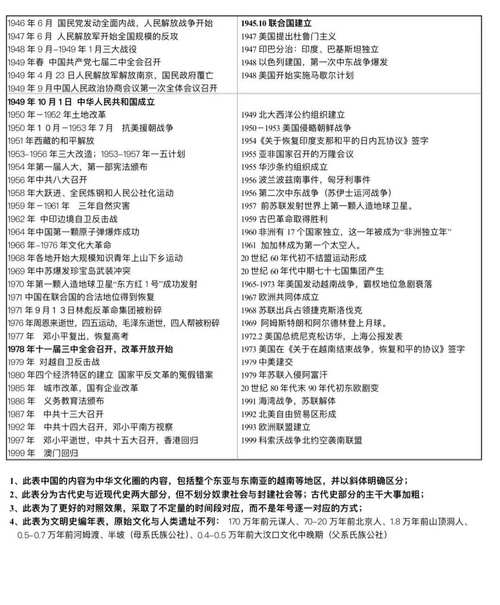
中国历史常识 | Chinese History: Key Facts (中英对照)
远古时期 | Prehistoric Period (c. 2.1 million BC – c. 2070 BC)
- 盘古开天辟地 - Pángǔ separates the sky from the earth
中国神话中开天辟地的神祇。 The deity in Chinese mythology who separated the sky from the earth.
- 三皇五帝 - Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors
中国传说中的“圣君”,被视为文明的开创者。 Legendary "sage-kings" credited with founding Chinese civilization.
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) - 黄帝 - Yellow Emperor (Huangdi)
被尊为“人文初祖”,传说中发明了文字、医学、舟车等。 Revered as the "ancestor of Chinese culture," credited with inventions like writing, medicine, and boats.
- 尧舜禹禅让 - Abdication of Yao, Shun, and Yu
传说中部落联盟首领通过让贤而非世袭的方式传递权力的制度。 A legendary system where the leader of the tribal alliance passed power to the most worthy person, not their heir.
- 大禹治水 - Yu the Great tames the floods
禹成功治理黄河水患,因此被推举为领袖,并建立了夏朝。 Yu successfully controlled the Yellow River floods, was chosen as leader, and founded the Xia Dynasty.
夏商周时期 | Xia, Shang, and Zhou Dynasties (c. 2070 BC – 256 BC)
- 夏朝 - Xia Dynasty (c. 2070–1600 BC)
中国史书记载的第一个世制制王朝。 The first dynasty recorded in Chinese historical texts.
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) - 商朝 - Shang Dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC)
中国第一个有直接文字(甲骨文)和考古证据(如殷墟)证实的王朝。 The first dynasty in China confirmed by both written records (oracle bone script) and archaeological evidence (e.g., Yin Ruins).
- 甲骨文 - Oracle Bone Script
刻在龟甲和兽骨上的早期汉字,用于占卜。 The earliest form of Chinese writing, inscribed on turtle shells and animal bones for divination.
- 周朝 - Zhou Dynasty (1046–256 BC)
- 中国历史上最长的王朝,分为西周和东周两个时期。 The longest-lasting dynasty in Chinese history, divided into the Western Zhou and Eastern Zhou periods.
- 分封制 - Enfeoffment System
周朝将土地和人民分封给亲属和功臣,建立诸侯国。 A system where the Zhou king granted land and people to relatives and meritorious officials, creating vassal states.
- 春秋战国 - Spring and Autumn Period & Warring States Period (770–221 BC)
东周的后半段,是一个社会大变革、思想大爆发的时期,出现了“百家争鸣”。 The latter part of the Eastern Zhou, a period of great social change and philosophical flourishing, known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought."
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) - 百家争鸣 - Hundred Schools of Thought
诸子百家(如儒家、道家、法家、墨家)思想相互争鸣的盛况。 A flourishing era where various philosophical schools (e.g., Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism, Mohism) competed and developed.
秦汉时期 | Qin and Han Dynasties (221 BC – 220 AD)
- 秦始皇 - First Emperor of Qin (Qin Shi Huang)
中国第一位皇帝,统一了六国。 The first emperor of China, who unified the six warring states.
- 统一度量衡、文字、货币 - Standardization of weights, measures, writing, and currency
秦始皇采取的重要措施,对中华文明的统一影响深远。 Key measures taken by the First Emperor that had a profound impact on the unification of Chinese civilization.
- 长城 - The Great Wall
为抵御北方游牧民族而修建的宏伟防御工事。 A massive fortification built to defend against northern nomadic tribes.
- 汉朝 - Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD)
中国历史上第一个黄金时代,汉族和汉字的名称由此而来。 China's first golden age; the names "Han Chinese" and "Han characters" derive from this dynasty.
- 丝绸之路 - The Silk Road
连接中国与中亚、欧洲的古代贸易路线,促进了东西方文化交流。 An ancient trade route connecting China with Central Asia and Europe, facilitating cultural exchange.
- 儒家思想 - Confucianism
由孔子创立,在汉代成为官方正统思想,影响中国两千多年。 Founded by Confucius, it became the state orthodoxy during the Han Dynasty and influenced China for over two millennia.
- 道教 - Taoism
中国本土的宗教和哲学,追求自然、无为而治。 China's native religion and philosophy, emphasizing nature and non-action (wu wei).
魏晋南北朝 | Wei, Jin, Northern and Southern Dynasties (220–589 AD)
- 三国时期 - Three Kingdoms Period (220–280 AD)
- 魏、蜀、吴三国鼎立的时期,充满战争和英雄故事。 A period of three rival states—Wei, Shu, and Wu—famous for warfare and heroic tales.
- 诸葛亮 - Zhuge Liang
蜀汉的丞相,以智慧和忠诚闻名。 The chancellor of Shu Han, famous for his wisdom and loyalty.
- 魏晋风度 - Wei-Jin style / Scholarly elegance
文人士大夫追求个性解放、清谈和艺术成就的时代风尚。 A cultural trend among scholars emphasizing personal freedom, philosophical discussions, and artistic pursuits.
- 佛教传入与兴盛 - Introduction and flourishing of Buddhism
佛教在这一时期从印度传入中国,并得到广泛传播。 Buddhism was introduced from India to China during this period and spread widely.
隋唐时期 | Sui and Tang Dynasties (581–907 AD)
- 隋朝 - Sui Dynasty (581–618 AD)
- 虽然短暂,但重新统一了中国,并开凿了大运河。 Although short-lived, it reunified China and built the Grand Canal.
- 唐朝 - Tang Dynasty (618–907 AD)
中国历史上另一个黄金时代,国力强盛,文化开放包容。 Another golden age of Chinese history, characterized by immense power and a cosmopolitan, inclusive culture.
- 长安 - Chang'an (modern-day Xi'an)
唐朝的都城,当时世界上最大、最繁华的国际都市之一。 The capital of the Tang Dynasty, one of the largest and most prosperous cities in the world at the time.
- 唐诗 - Tang Poetry
中国古典诗歌的巅峰,涌现了李白、杜甫等伟大诗人。 The pinnacle of classical Chinese poetry, with great poets like Li Bai and Du Fu.
- 科举制度 - Imperial Examination System
隋朝创立,唐朝完善,通过考试选拔官员的制度,打破了贵族对官场的垄断。 A system to select officials through examinations, founded in the Sui and perfected in the Tang, breaking the nobility's monopoly on power.
宋元时期 | Song and Yuan Dynasties (960–1368 AD)
- 宋朝 - Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD)
- 分为北宋和南宋,经济、科技和文化高度发达,但军事实力相对较弱。 Divided into Northern and Southern Song, it was an era of high economic, technological, and cultural development, but with relatively weak military power.
- 四大发明 - The Four Great Inventions
- 造纸术、印刷术、火药、指南针 - Papermaking, Printing, Gunpowder, and the Compass
- 这四项发明对世界文明的进程产生了巨大影响。 These four inventions had a massive impact on the course of world civilization.
- 理学 - Neo-Confucianism
儒学的新发展阶段,强调“理”和“格物致知”。 A new development of Confucianism that emphasized "Principle" (Li) and "investigating things to extend knowledge."
- 元朝 - Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368 AD)
- 由蒙古族建立,是中国历史上第一个由少数民族建立的大一统王朝。 Founded by the Mongols, it was the first unified dynasty in Chinese history established by a non-Han ethnic group.
- 马可·波罗 - Marco Polo
- 威尼斯旅行家,他的《马可·波罗游记》向西方介绍了中国的繁荣。 A Venetian traveler whose Travels of Marco Polo introduced the prosperity of China to the West.
明清时期 | Ming and Qing Dynasties (1368–1912 AD)
- 明朝 - Ming Dynasty (1368–1644 AD)
- 汉族建立的最后一个大一统王朝,以恢复汉族传统和强大的海军著称。 The last unified dynasty founded by the Han, known for restoring Han traditions and its powerful navy.
- 郑和下西洋 - Zheng He's voyages
明朝太监郑和率领庞大船队七次下西洋,途经东南亚、印度洋直至非洲东岸。 Eunuch Zheng He led massive fleets on seven voyages to the "Western Oceans," reaching Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean, and the east coast of Africa.
- 紫禁城 - The Forbidden City
位于北京,是明清两代的皇宫,现为故宫博物院。 Located in Beijing, it was the imperial palace for the Ming and Qing dynasties, now the Palace Museum.
- 清朝 - Qing Dynasty (1644–1912 AD)
- 由满族建立,是中国最后一个封建王朝。 Founded by the Manchu, it was the last imperial dynasty in China.
- 康乾盛世 - Kangxi-Qianlong Golden Age
康熙、雍正、乾隆三位皇帝在位期间,清朝国力达到顶峰。 A period of peak prosperity and power under the reigns of the emperors Kangxi, Yongzheng, and Qianlong.
- 闭关锁国 - Closed-door policy
清朝中后期实行的限制对外交流的政策,导致中国逐渐落后于世界。 A policy of restricting foreign contact that led to China's gradual fall behind the rest of the world.
- 鸦片战争 - Opium Wars (1839–1842, 1856–1860)
英国等西方列强为打开中国市场而对中国发动的侵略战争,标志着中国近代史的开端。 Wars initiated by Western powers like Britain to force open China's market, marking the beginning of modern Chinese history.
近现代 | Modern and Contemporary China (1912 AD – Present)
- 中华民国 - Republic of China (1912–1949)
推翻清朝后建立的亚洲第一个共和国。 The first republic in Asia, established after the fall of the Qing Dynasty.
- 新文化运动 - New Culture Movement (c. 1915–1925)
一场思想解放运动,提倡民主与科学,反对封建思想。 A movement for intellectual emancipation that promoted "Democracy" and "Science" and opposed feudal ideas.
- 中华人民共和国成立 - Founding of the People's Republic of China (1949)
毛泽东在北京天安门城楼宣告中华人民共和国成立。 Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the PRC on the Tiananmen Gate in Beijing.
- 改革开放 - Reform and Opening-Up (1978–present)
由邓小平发起的经济改革政策,使中国经济迅速发展,融入全球经济。 An economic reform policy initiated by Deng Xiaoping that led to rapid economic development and China's integration into the global economy.
- 香港/澳门回归 - Handover of Hong Kong/Macau (1997/1999)
香港于1997年、澳门于1999年分别回归中国。 Hong Kong returned to China in 1997, and Macau in 1999.
- 北京奥运会 - Beijing Olympics (2008)
中国首次举办夏季奥运会,向世界展示了其发展成就。 China's first time hosting the Summer Olympics, showcasing its development to the world.











